Understanding the Need for Safety Locks on Bottled Loading Water Dispensers
Bottled loading water dispensers provide convenient access to both hot and cold water, making them a common fixture in homes, offices, and public facilities. However, the hot water function presents potential safety risks, especially for children and elderly users. Accidental activation of the hot water tap can result in scalding injuries due to the high temperatures typically used for tea, coffee, or sterilization purposes. To address these concerns, manufacturers incorporate various safety lock mechanisms designed to prevent unintentional operation. Understanding how these locks work and their importance in overall product design is essential for safe and reliable usage.
Types of Safety Lock Mechanisms in Hot Water Dispensers
Different water dispenser models employ a variety of safety lock designs, each aimed at reducing the chance of accidental dispensing of hot water. These mechanisms may include button locks, lever locks, dual-step activation systems, and child-proof switches. Each design functions by requiring an additional deliberate action before hot water can flow, ensuring that users cannot accidentally activate the hot water spout by a simple touch. The selection of safety lock type often depends on user demographics, dispenser structure, and the intended use environment such as residential or commercial settings.
Button Lock Mechanisms
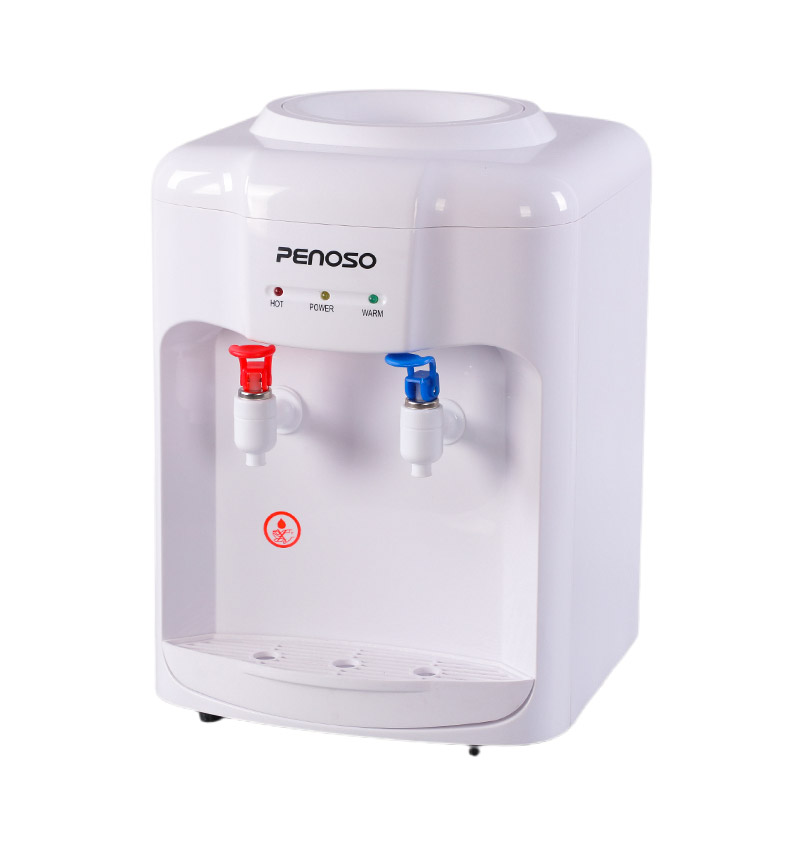
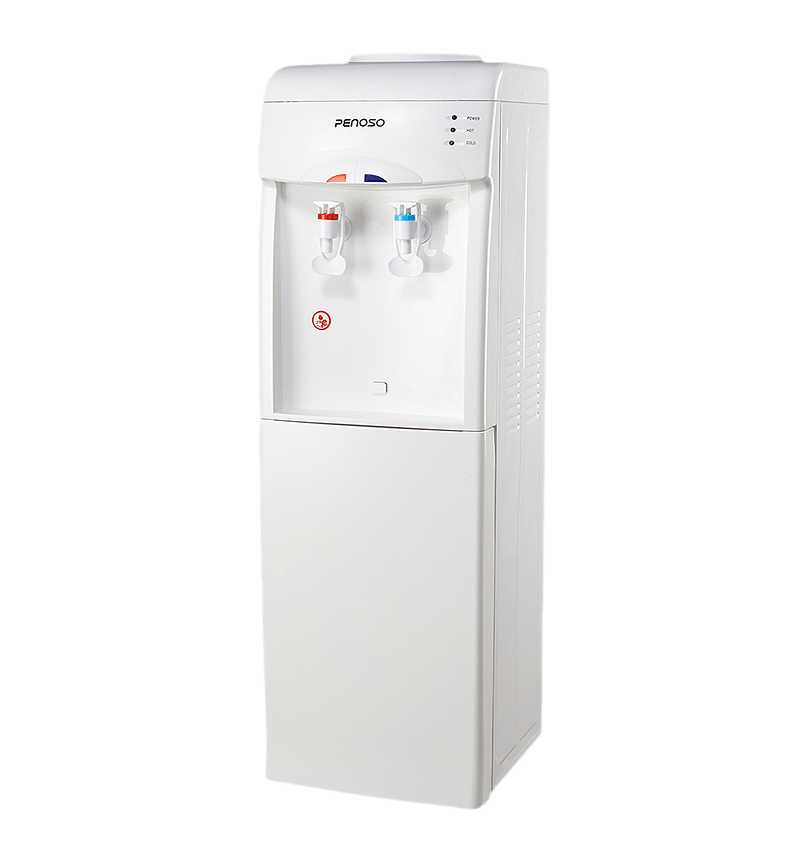
One of the most common types of safety locks on bottled loading water dispensers is the button lock mechanism. This design requires the user to press a safety button simultaneously while pushing the hot water lever. The dual-motion process ensures that only intentional use triggers water flow. For example, to dispense hot water, the user must hold down a red button and press the lever downward. This simple yet effective method prevents children or unaware users from accidentally scalding themselves. Button locks are widely used in household models where accessibility and safety must coexist.
Lever Lock and Lift-to-Unlock Designs
Lever locks are mechanical safety systems that restrict the lever’s downward motion until a specific action, such as lifting or sliding, is performed. The lift-to-unlock design requires the user to lift the lever slightly before pressing it down to release hot water. This additional movement prevents unintentional dispensing caused by accidental bumps or weight pressure. Lever locks are durable, cost-effective, and easy to operate for adults while still providing adequate protection for children. Many manufacturers integrate this design in bottled loading water dispensers for office environments where multiple users access the same unit.
Dual-Step Activation Systems
Dual-step systems combine mechanical and electrical safety features to enhance user protection. These systems require the user to perform two distinct actions, such as pressing a safety switch before engaging the dispensing lever. Some models include an electronic delay function, allowing water to flow only after the button is held for a few seconds. This ensures the user’s intention is deliberate and eliminates quick accidental touches. Dual-step activation is frequently found in high-end or public-use water dispensers where enhanced safety measures are required due to higher user traffic and varying user awareness.
Child-Proof Safety Switches
Child-proof safety switches are specifically designed to prevent children from accidentally dispensing hot water. These switches are often positioned at the back or top of the dispenser to be out of reach for small children. Some versions use a slide-lock mechanism that must be toggled to unlock the hot water function. Other designs rely on digital controls requiring a combination of button presses to activate. This feature is particularly useful in households, schools, and daycare facilities where young users are present. Such safety mechanisms reduce the likelihood of accidents without compromising ease of access for adults.
Temperature Regulation and Safety Integration
Beyond mechanical locks, temperature control plays an important role in safety management. Many bottled loading water dispensers now include thermostatic controls that limit the maximum water temperature. Even if a user accidentally triggers hot water flow, the temperature remains within a safe range. Some models incorporate sensors that automatically shut off the heating element when the water reaches a certain level. Combining these thermal safety features with physical locks provides a comprehensive safety system that minimizes scalding risks and improves user confidence.
Comparison Table of Common Safety Lock Types
The following table compares several safety lock mechanisms commonly found in bottled loading water dispensers, highlighting their primary characteristics and usage scenarios.
| Safety Lock Type | Activation Method | Primary Advantage | Common Usage Environment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Button Lock | Press button + push lever simultaneously | Prevents accidental activation through dual motion | Households, offices |
| Lever Lock | Lift or slide lever before pressing | Mechanical simplicity and durability | Offices, commercial areas |
| Dual-Step System | Press safety switch + engage lever | Enhanced protection with electrical control | Public and industrial environments |
| Child-Proof Switch | Toggle or hidden button placement | Prevents child access effectively | Homes, schools, childcare centers |
| Thermostatic Safety | Automatic temperature regulation | Maintains safe water temperature limits | Residential and commercial dispensers |
Materials and Durability Considerations
The reliability of a safety lock system depends not only on its design but also on the materials used. High-quality bottled loading water dispensers utilize heat-resistant plastics or stainless steel for critical components, ensuring stability under continuous thermal stress. Buttons and levers are often reinforced to withstand repeated use, while seals are made from silicone or rubber to prevent leaks. Some models employ food-grade plastics compliant with safety standards to prevent chemical leaching at high temperatures. Regular maintenance of these components ensures the long-term integrity of the safety lock system.
Maintenance and Inspection of Safety Locks
Proper maintenance of safety locks ensures consistent performance. Users should periodically inspect the locking mechanism for signs of wear, stiffness, or corrosion. Dust or mineral deposits can accumulate around the button or lever area, impeding smooth operation. Cleaning with mild detergent and soft cloth prevents residue buildup. If the dispenser has electronic safety switches, users should test them regularly to confirm response time and function. Timely maintenance not only prolongs the dispenser’s life but also guarantees that safety mechanisms operate as intended during daily use.
Integration of Electronic and Mechanical Safety Systems
Modern bottled loading water dispensers increasingly combine electronic and mechanical safety systems to provide layered protection. An example is an electric hot water tap that remains locked until both a button is pressed and a proximity sensor detects a user’s hand within range. Some designs include child-safety timers that disable hot water dispensing for a period of inactivity. The integration of sensors, microcontrollers, and mechanical locks allows for precise control over when and how hot water can be dispensed. This hybrid approach ensures operational efficiency while maintaining a high standard of user safety.
User Awareness and Safety Education
Even with reliable safety locks, user education plays a crucial role in preventing scalding accidents. Clear labeling and color coding of hot and cold taps reduce confusion, especially in shared environments. Instruction manuals should emphasize safe operating practices, such as keeping children away from dispensers and avoiding direct contact with spouts. In workplaces or public settings, periodic training or signage reminders can reinforce safe handling. Encouraging responsible use and awareness ensures that the safety locks function as part of a broader safety culture rather than relying solely on mechanical protection.
Advancements in Safety Lock Technology
Continuous technological development has led to new safety lock innovations in bottled loading water dispensers. Some manufacturers are introducing magnetic locks that disengage only when the user holds a magnetic key near the dispenser. Others are exploring biometric safety features such as fingerprint activation for restricted access in industrial or laboratory settings. These advancements enhance precision and allow customized user access while maintaining operational convenience. Although such technologies may increase production costs, they offer long-term safety benefits in environments where hot water use must be carefully controlled.
Comparison Table: Mechanical vs Electronic Safety Locks
To better understand their practical differences, the following table compares mechanical and electronic safety lock systems based on function, maintenance, and reliability.
| Feature | Mechanical Lock | Electronic Lock |
|---|---|---|
| Activation Method | Manual action (lift, press, slide) | Digital control (button or sensor) |
| Power Requirement | None | Requires electricity or battery |
| Maintenance | Low, periodic cleaning | Moderate, includes sensor calibration |
| Durability | High under physical stress | Depends on circuit protection |
| Cost | Lower initial expense | Higher due to electronic components |
| Application | Common in household and office dispensers | Used in advanced or public systems |
Ensuring Compliance with Safety Standards
Manufacturers of bottled loading water dispensers must comply with international safety standards and certifications. These include guidelines that regulate maximum water temperature, electrical insulation, and mechanical safety design. Certifications such as UL, CE, or RoHS ensure that the product has undergone rigorous testing for user protection. Compliance with these standards not only enhances consumer trust but also reduces liability risks associated with accidents. Regular audits and safety testing further confirm that lock mechanisms meet operational safety expectations under prolonged use.
Future Trends in Hot Water Safety Design
Future developments in bottled loading water dispensers are expected to focus on smart safety integration and automation. Internet-connected dispensers may include programmable temperature limits, automatic lock activation after idle periods, and usage tracking for maintenance alerts. Advances in sensor technology will allow precise user detection, ensuring hot water is dispensed only under safe conditions. As safety expectations evolve, manufacturers will continue to combine mechanical reliability with intelligent control systems to create safer, more efficient, and user-friendly water dispensing solutions.



 English
English عربى
عربى Português
Português Español
Español.jpg)